Comprehensive Guide to Alemtuzumab: Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, and More
What is Alemtuzumab?
Overview of Alemtuzumab
Generic Name: Alemtuzumab
Brand Name: Campath (CLL), Lemtrada (MS), MabCampath (Europe, CLL)
Drug Group: Monoclonal antibody; anti-CD52 immunotherapy
Commonly Used For
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in adults, particularly B-cell CLL.
- Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) in adults with active disease.
- Off-label uses for other conditions like T-cell lymphomas or transplant rejection under specialist guidance.
Key Characteristics
Form: Intravenous infusion (10 mg/mL or 30 mg/mL vials).
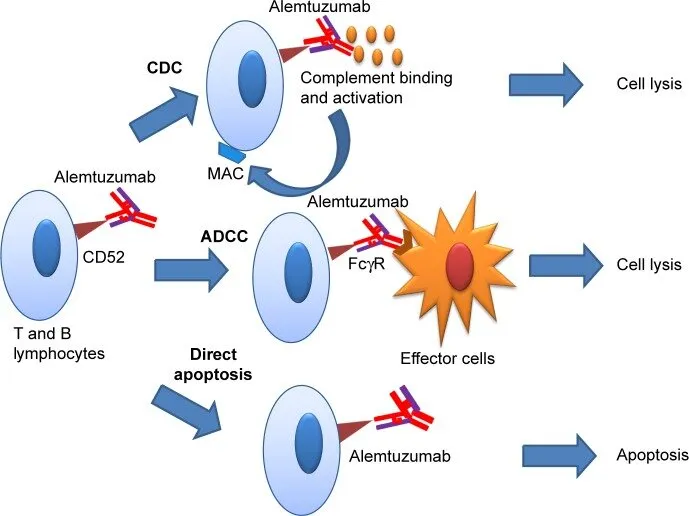
Mechanism: Binds CD52, causing lysis of B and T lymphocytes via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-mediated cytotoxicity.
Approval: FDA-approved (2001 for Campath, 2014 for Lemtrada) and EMA-approved for CLL and MS.
Indications and Uses of Alemtuzumab
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Treats B-cell CLL in adults, particularly those with relapsed or refractory disease, improving progression-free survival.
Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis (RRMS): Reduces relapse rates and disability progression in adults with active disease, typically after other MS therapies fail.
Off-Label Uses: May be used in T-cell lymphomas, autoimmune cytopenias, or to prevent transplant rejection under specialist supervision.
Dosage of Alemtuzumab
Dosage for Adults
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (Campath):
- Dose Escalation: Start with 3 mg IV daily, increasing to 10 mg, then 30 mg daily as tolerated (usually over 3–7 days).
- Maintenance: 30 mg IV three times weekly (e.g., Monday, Wednesday, Friday) for up to 12 weeks.
Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis (Lemtrada):
- First Course: 12 mg/day IV for 5 consecutive days (total 60 mg).
- Second Course: 12 mg/day IV for 3 consecutive days (total 36 mg), 12 months after the first course.
- Additional Courses: May be given as needed (12 mg/day for 3 days) if disease activity persists, at least 12 months apart.
Dosage for Children
Not approved for pediatric use; limited data exist for off-label use in rare conditions under specialist oversight.
Dosage for Pregnant Women
Pregnancy Category C: Avoid due to potential fetal harm; use effective contraception during and for 4 months after treatment. Consult a specialist.
Dosage Adjustments
Infusion Reactions: Pause or reduce infusion rate for severe reactions; premedicate with corticosteroids, antihistamines, or acetaminophen.
Infections: Interrupt therapy if serious infections occur; resume only after resolution.
Renal/Hepatic Impairment: No specific adjustments; monitor closely for toxicity.
Additional Considerations
- Administer in a facility equipped for managing infusion reactions.
- Premedication (e.g., methylprednisolone) and prophylaxis (e.g., antivirals, antibiotics) are required to reduce risks.
How to Use Alemtuzumab
Administration: The drug is given as an IV infusion over 2–4 hours in a hospital or infusion center. For CLL, infusions occur three times weekly; for MS, infusions follow a 5-day or 3-day course.
Premedication: Administer corticosteroids (e.g., methylprednisolone), antihistamines, and acetaminophen 30–60 minutes before infusion to reduce reactions.
Monitoring: Continuous monitoring for infusion reactions (e.g., fever, rash, hypotension) during and for 2 hours post-infusion.
Missed Dose: Not applicable, as the therapy is administered by professionals on a strict schedule.
Additional Tips:
- Stay hydrated and report symptoms like fever or rash immediately.
- Complete all required blood tests and follow-up appointments.
Contraindications for Alemtuzumab
Patients with hypersensitivity to Alemtuzumab or its components.
Those with active infections, including tuberculosis (TB) or hepatitis B/C.
Patients with HIV or severe immunosuppression (except in controlled settings for CLL).
Those with active or recent malignancies (other than CLL).
Warnings & Precautions for Alemtuzumab
General Warnings
Infusion Reactions: Severe reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, hypotension, bronchospasm) may occur; monitor closely during infusion.
Infections: The drug increases risk of serious infections (e.g., CMV, Pneumocystis pneumonia, TB). Screen for TB and hepatitis before treatment; use prophylactic antivirals/antibiotics.
Autoimmune Disorders: Risk of immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), autoimmune hemolytic anemia, or thyroid disorders; monitor blood counts and thyroid function.
Stroke and Cardiovascular Events: Rare but serious; increased risk in MS patients within 3 days of infusion.
Malignancies: Increased risk of thyroid cancer, melanoma, and lymphoproliferative disorders; regular screening is essential.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy: Category C; avoid due to fetal harm risk. Use contraception during and for 4 months post-treatment.
Breastfeeding: Unknown if excreted in breast milk; avoid breastfeeding during and for 4 months after therapy.
Elderly: Increased risk of infections and infusion reactions; monitor closely.
Children: Not approved; safety data are limited.
Immunocompromised Patients: Extreme caution due to infection risk.
Additional Precautions
- Inform your doctor about all medical conditions, especially infections, autoimmune diseases, or recent vaccinations.
- Avoid live vaccines during and for 3 months after treatment.
Overdose and Management of Alemtuzumab
Overdose Symptoms
Overdose is rare due to controlled administration but may cause:
- Severe infusion reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, hypotension).
- Increased risk of infections or autoimmune complications.
- Bone marrow suppression (e.g., neutropenia, thrombocytopenia).
Immediate Actions
Stop Infusion: Discontinue immediately if overdose is suspected.
Supportive Care: Manage symptoms (e.g., fluids for hypotension, corticosteroids for reactions).
Monitor: Check blood counts, vital signs, and infection status.
Additional Notes
- Overdose risk is minimized by administration in clinical settings.
- Store the medication securely to prevent misuse.
Side Effects of Alemtuzumab
Common Side Effects
- Infusion reactions (fever, chills, rash; 70–90%)
- Fatigue (10–34%)
- Nausea or vomiting (21–25%)
- Headache (13–24%)
- Infections (e.g., upper respiratory; 16–53%)
These effects are often transient but require monitoring.
Serious Side Effects
Seek immediate medical attention for:
Infections: Fever, cough, or signs of opportunistic infections (e.g., CMV, PCP).
Autoimmune Disorders: Bruising, bleeding (ITP), or jaundice (hemolytic anemia).
Neurologic: Stroke symptoms (e.g., sudden weakness, speech difficulty).
Allergic Reactions: Anaphylaxis, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
Cardiovascular: Chest pain or irregular heartbeat.
Additional Notes
- Regular blood tests (CBC, thyroid function) are critical for long-term safety.
- Side effects may persist months after treatment due to prolonged lymphopenia.
Drug Interactions with Alemtuzumab
The therapy may interact with:
- Immunosuppressants (e.g., Cyclosporine, Tacrolimus): Increase infection risk; monitor closely.
- Live Vaccines: Contraindicated due to risk of vaccine-related infections.
- Other Biologics (e.g., Rituximab): May enhance immunosuppression; avoid coadministration.
- Antiviral/Antibiotic Prophylaxis: Required to prevent infections; no significant adverse interactions.
Patient Education or Lifestyle
Treatment Adherence: Attend all infusion appointments and follow-up visits for blood tests (monthly for MS patients, up to 48 months post-treatment).
Infection Prevention: Wash hands frequently, avoid sick contacts, and report fever or infection signs immediately.
Vaccinations: Complete non-live vaccines (e.g., flu, pneumococcal) at least 6 weeks before starting the drug; avoid live vaccines.
Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy diet and avoid smoking to support immune recovery. Limit alcohol due to liver risks.
Monitoring: Watch for signs of autoimmune disorders (e.g., easy bruising, fatigue) or stroke (e.g., sudden headache, weakness).
Travel: Avoid areas with high infection risk (e.g., TB-endemic regions); consult your doctor for prophylaxis.
Pharmacokinetics of Alemtuzumab
Absorption: Administered IV; not applicable for oral absorption.
Distribution: Volume of distribution is ~0.18 L/kg; primarily binds CD52 on lymphocytes.
Metabolism: Degraded via proteolysis; no significant hepatic metabolism.
Excretion: Cleared as peptide fragments; negligible renal excretion.
Half-Life: ~2–14 days, with prolonged pharmacodynamic effects (lymphocyte depletion for 6–12 months).
Pharmacodynamics of Alemtuzumab
Alemtuzumab exerts its effects by:
- Binding CD52 on B and T lymphocytes, natural killer cells, and monocytes, inducing cell lysis via ADCC and complement activation.
- Depleting lymphocytes, reducing immune-mediated damage in MS and leukemic cells in CLL.
- Causing prolonged lymphopenia, requiring long-term monitoring for infections and autoimmune conditions.
- Modulating immune reconstitution, contributing to sustained MS remission.
Storage of Alemtuzumab
- Temperature: Store vials in a refrigerator (2–8°C or 36–46°F); do not freeze.
- Protection: Keep in original carton to protect from light; do not shake vials.
- Safety: Store securely in clinical settings to prevent misuse; only healthcare professionals should handle.
- Disposal: Follow local regulations or consult a pharmacist for safe disposal of unused medication.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What conditions does Alemtuzumab treat?
A: The drug treats chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS).
Q: Can Alemtuzumab increase infection risk?
A: Yes, the medication significantly increases infection risk; prophylaxis and monitoring are required.
Q: How is Alemtuzumab administered?
A: The therapy is given as an IV infusion over 2–4 hours in a clinical setting with premedication.
Q: Is Alemtuzumab safe during pregnancy?
A: Category C; avoid due to fetal harm risk. Use contraception during and for 4 months post-treatment.
Q: How long do Alemtuzumab’s effects last?
A: Lymphocyte depletion may last 6–12 months, requiring long-term monitoring.
Regulatory Information
The medication is approved by:
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Approved in 2001 (Campath for CLL) and 2014 (Lemtrada for MS, under REMS).
European Medicines Agency (EMA): Approved for CLL (MabCampath) and MS (Lemtrada).
Other Agencies: Approved globally (e.g., Drug Administration of Vietnam) for similar indications; consult local guidelines.
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2023). Lemtrada (Alemtuzumab) Prescribing Information.
- Official FDA documentation detailing the drug’s approved uses, dosage, and safety for MS.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). (2023). Lemtrada (Alemtuzumab) Summary of Product Characteristics.
- EMA’s comprehensive information on the medication’s indications and precautions in Europe.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2023). Alemtuzumab: MedlinePlus Drug Information.
- NIH resource providing detailed information on the drug’s uses, side effects, and precautions.
- World Health Organization (WHO). (2023). WHO Model List of Essential Medicines: Alemtuzumab.
- WHO’s inclusion of Alemtuzumab as an essential medicine for CLL and MS.
- New England Journal of Medicine. (2012). Alemtuzumab for Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis.
- Peer-reviewed study on the medication’s efficacy in MS (note: access may require a subscription).
