Gastric Cancer: Signs, Causes, and Treatment
Overview of Gastric Cancer
Gastric cancer refers to abnormal and uncontrolled growth of cells at any location within the stomach. Tumors can arise anywhere but most frequently originate from glandular tissue lining the stomach’s inner surface.
Stages of Gastric Cancer
- Stage 0 (Early stage): Malignant cells are confined to the stomach mucosa.
- Stage I: Cancer cells invade the second layer of the stomach; symptoms are often absent.
- Stage II: Cancer penetrates through the mucosa; patients may experience abdominal pain, nausea, etc.
- Stage III: Cancer spreads to lymph nodes and nearby organs.
- Stage IV: Cancer metastasizes widely, associated with high mortality risk.
Symptoms of Gastric Cancer
Early-Stage Symptoms
Often nonspecific and easily mistaken for other gastrointestinal conditions:
- Indigestion;
- Bloating after meals;
- Heartburn;
- Mild nausea;
- Loss of appetite.
Advanced Symptoms
As the tumor enlarges, more serious manifestations may appear:
- Abdominal pain;
- Persistent nausea and vomiting;
- Heartburn;
- Difficulty swallowing;
- Continuous bloating;
- Unexplained weight loss;
- Early satiety (feeling full after small meals);
- Blood in stool;
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin/eyes);
- Fatigue;
- Postprandial stomach pain.
Gastric tumors can be life-threatening if malignant. The disease often progresses silently and may metastasize if not diagnosed and treated promptly.

When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of the above symptoms, seek medical advice immediately. Early diagnosis and intervention reduce disease severity and improve recovery. Individual conditions vary; always discuss diagnostic and treatment options with your physician.
Causes of Gastric Cancer
Although the exact cause of uncontrolled cell growth in the stomach is unknown, several risk factors have been identified:
- Unhealthy diet: Frequent consumption of fast foods, fried or grilled items, pickled vegetables, and canned products.
- Poor eating habits: Eating too quickly or insufficient chewing.
- Helicobacter pylori infection: Causes gastritis and ulcers, increasing cancer risk.
- History of gastric disease or surgery.
- Genetic predisposition: Family history of gastric cancer.
- Other factors: Age, sex, environment, alcohol, smoking, obesity, and chronic stress.
Risk Factors for Gastric Cancer
Who is at Higher Risk?
While anyone can develop gastric cancer, the following groups face greater risk:
- Blood group A;
- Men;
- Individuals ≥50 years old.
Additional Risk-Enhancing Factors:
- Chronic H. pylori–related ulcers.
- Recurrent gastritis or peptic ulcers.
- Living in polluted environments or frequent exposure to carcinogens.
- Family history of gastric cancer.
- Smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Overweight or obesity.
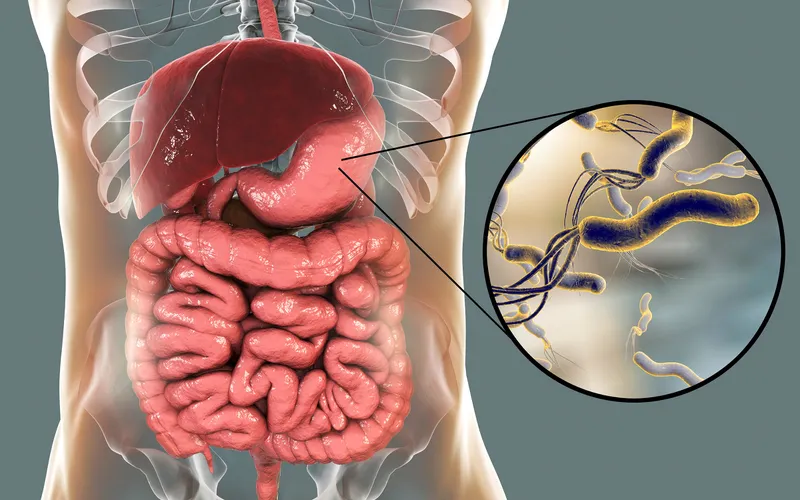
Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastric Cancer
Diagnostic Methods
If gastric cancer is suspected, physicians will conduct history-taking and a physical examination. Further tests may include:
- Blood tests: Detect tumor markers.
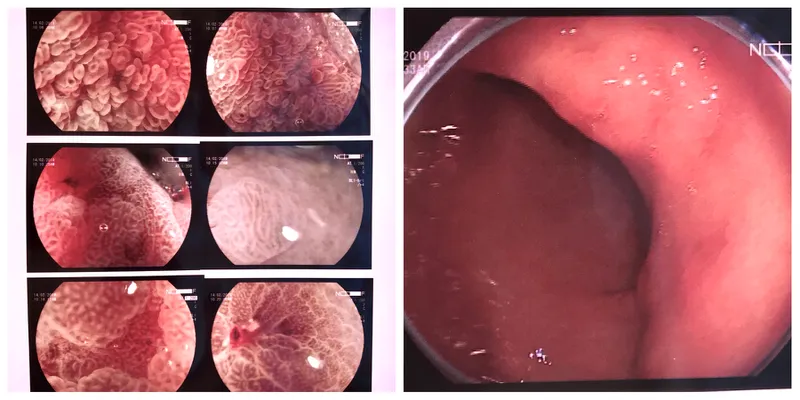
- Upper endoscopy: Flexible endoscope with a camera to visualize the stomach and identify polyps or abnormal cells.
- Imaging (CT, X-ray, MRI): Evaluate tumor size, location, invasiveness, and metastasis.
- Biopsy: Sampling of abnormal tissue to confirm malignancy.
Early diagnosis enables timely treatment and improved prognosis.
Treatment Options
Therapeutic strategies depend on the stage and histological type:
- Surgery: Partial or total gastrectomy to remove affected tissue.
- Chemotherapy: Systemic agents to destroy cancer cells or control tumor growth; supportive medications are often required to manage side effects.
- Radiotherapy: High-energy beams to kill or slow cancer cells, especially when metastasis to bones or brain occurs.
- Immunotherapy/Targeted therapy: Vaccines or targeted drugs may be recommended in specific cases.
Lifestyle and Prevention of Gastric Cancer
Dietary Measures
- Drink adequate water.
- Increase intake of green vegetables, fruits, whole grains, protein-rich foods, and high-fiber meals.
- Limit high-fat foods.
- Reduce consumption of canned, smoked, or pickled products.
Lifestyle Habits
- Adhere to medical advice during treatment.
- Maintain a positive lifestyle and minimize stress.
- Report any new or unusual symptoms promptly.
- Attend regular follow-ups for monitoring and timely treatment adjustments.
Effective Preventive Strategies
- Exercise regularly to strengthen immunity.
- Quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke.
- Abstain from alcohol.
- Follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting processed or pickled foods.
- Maintain a healthy weight and lose excess weight if needed.
- Undergo regular cancer screening for early detection and treatment.

