Comprehensive Guide to Amphotericin B: Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, and More
What is Amphotericin B?
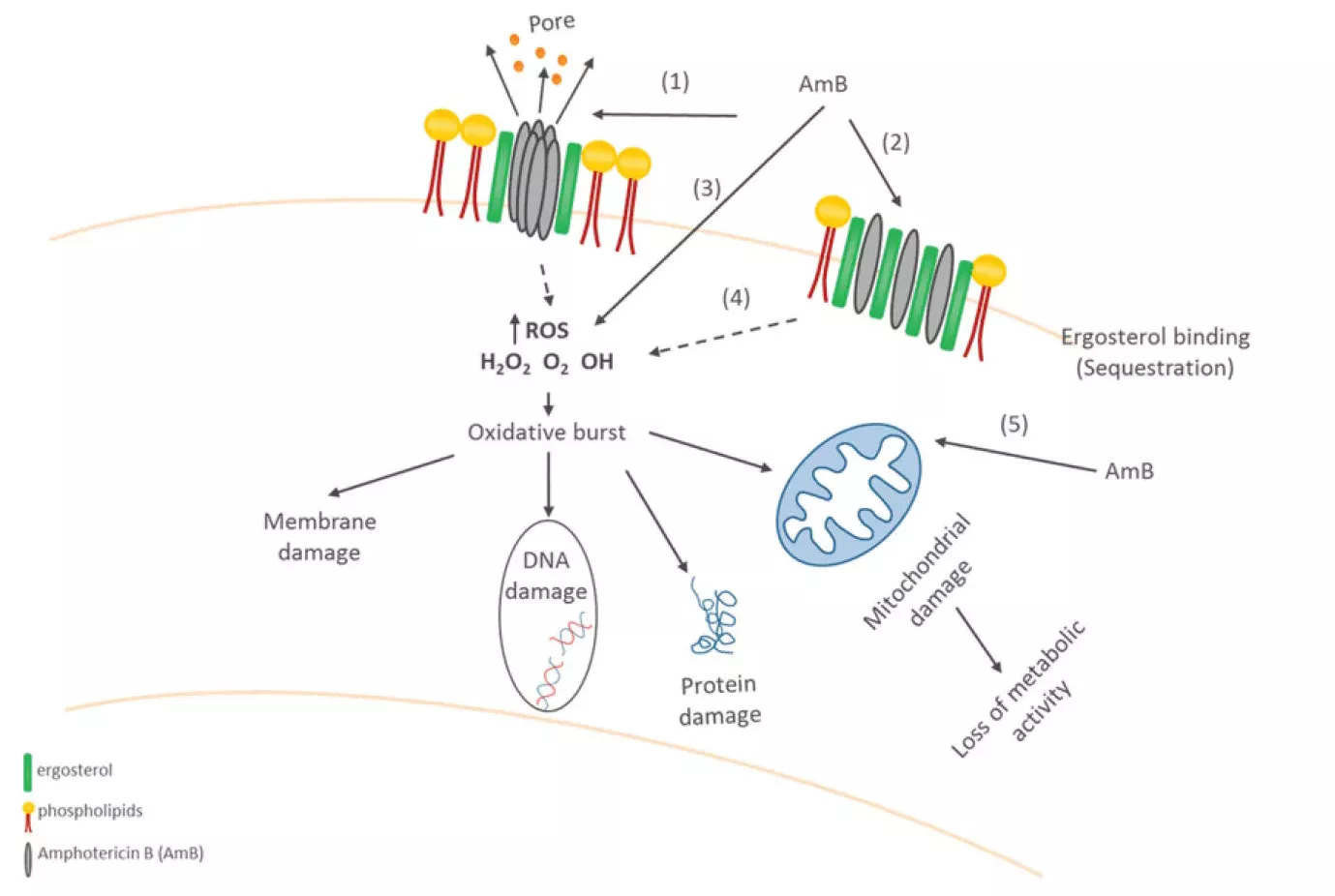
Overview of Amphotericin B
Generic Name: Amphotericin B
Brand Name: Fungizone (conventional), AmBisome (liposomal), Abelcet (lipid complex), generics
Drug Group: Polyene antifungal
Commonly Used For
- Treat systemic fungal infections (e.g., candidemia, aspergillosis, cryptococcosis).
- Manage severe mucocutaneous candidiasis or fungal meningitis.
- Treat visceral leishmaniasis (liposomal form).
- Off-label uses include fungal keratitis or prophylaxis in immunocompromised patients under specialist guidance.
Key Characteristics
Form: IV powder for reconstitution (50 mg/vial) in conventional or lipid formulations.
Mechanism: Binds to ergosterol, creating pores in fungal membranes, causing leakage and cell death.
Approval: FDA-approved (1958 for Fungizone) and EMA-approved for systemic fungal infections.
Indications and Uses of Amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is indicated for:
Systemic Fungal Infections: Treats candidiasis, aspergillosis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, and mucormycosis.
Fungal Meningitis: Manages cryptococcal meningitis, often with flucytosine.
Visceral Leishmaniasis: Liposomal form is the first-line treatment.
Off-Label Uses: Prophylaxis in neutropenic patients or treatment of rare fungal infections (e.g., blastomycosis) under specialist supervision.
Dosage of Amphotericin B
Dosage for Adults
Conventional (Fungizone):
- 0.25–1 mg/kg/day IV (maximum 1.5 mg/kg/day) over 2–6 hours.
- Initial test dose: 1 mg IV over 20–30 minutes to assess tolerance.
Liposomal (AmBisome): 3–5 mg/kg/day IV (up to 10 mg/kg/day for invasive aspergillosis or cryptococcosis).
Lipid Complex (Abelcet): 5 mg/kg/day IV.
Visceral Leishmaniasis (Liposomal): 3–5 mg/kg/day on days 1–5, then 3–5 mg/kg on days 14 and 21 (total 12–15 mg/kg).
Dosage for Children
Conventional: 0.25–1 mg/kg/day IV (maximum 1.5 mg/kg/day).
Liposomal: 3–5 mg/kg/day IV, adjusted per weight and tolerance.
Test Dose: 0.1–0.25 mg/kg (maximum 1 mg) to assess infusion reactions.
Dosage for Pregnant Women
Pregnancy Category B (Liposomal) / C (Conventional): Limited data; use only if benefits outweigh risks. Consult an infectious disease specialist.
Dosage Adjustments
Renal Impairment: Reduce dose or extend interval in conventional form (e.g., 0.5–0.7 mg/kg every 24–48 hours); liposomal forms are less nephrotoxic, so adjustments are less common.
Hepatic Impairment: No specific adjustments; monitor liver function.
Elderly: Start with lower doses; monitor for renal and infusion reactions.
Additional Considerations
- Administer IV infusions with pre-medication (e.g., antihistamines, antipyretics) to reduce infusion reactions.
- Monitor serum creatinine, electrolytes (potassium, magnesium), and complete blood count regularly.
How to Use Amphotericin B
Administration:
- IV Infusion: Reconstitute powder with sterile water; dilute in 5% dextrose (not saline); infuse over 2–6 hours.
- Test Dose: Administer 1 mg (conventional) or 0.1–0.25 mg/kg (liposomal) to assess tolerance.
Timing: Follow prescribed schedule (once daily or as adjusted).
Monitoring: Check for infusion reactions (e.g., fever, chills) and renal function during and after administration.
Additional Tips:
- Ensure adequate hydration to protect kidney function.
- Report symptoms like hearing loss, swelling, or severe chills immediately.
Contraindications for Amphotericin B
The antifungal is contraindicated in:
- Patients with hypersensitivity to Amphotericin B or its components.
- Patients with severe renal failure (unless benefits outweigh risks with lipid formulations).
Warnings & Precautions for Amphotericin B
General Warnings
Nephrotoxicity: Risk of kidney damage; monitor creatinine and urine output regularly.
Infusion Reactions: Fever, chills, or hypotension may occur; pre-medicate with antipyretics or corticosteroids.
Electrolyte Imbalance: Risk of hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia; monitor and supplement if needed.
Anemia: Bone marrow suppression may cause anemia; monitor hemoglobin.
Hepatotoxicity: Rare; monitor liver function tests.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy: Category B (liposomal) or C (conventional); use cautiously with specialist consultation.
Breastfeeding: Excreted in breast milk in small amounts; weigh benefits versus risks.
Elderly: Increased risk of renal and infusion reactions; use lower doses.
Children: Approved with adjusted dosing; monitor for toxicity.
Renal Impairment: High risk with conventional form; prefer liposomal forms.
Additional Precautions
- Inform your doctor about kidney disease, electrolyte imbalances, or previous antifungal reactions before starting the medication.
- Avoid rapid infusion to minimize adverse reactions.
Overdose and Management of Amphotericin B
Overdose Symptoms
- Severe hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia.
- Acute kidney injury or renal failure.
- Severe infusion reactions (e.g., shock, arrhythmias).
Immediate Actions
Contact Emergency Services: Stop infusion; seek immediate medical intervention.
Supportive Care: Correct electrolytes, provide hydration, and monitor renal function.
Hemodialysis: May be considered in severe cases; consult a specialist.
Additional Notes
- Overdose is rare with proper dosing; ensure accurate weight-based calculations.
- Report persistent symptoms promptly.
Side Effects of Amphotericin B
Common Side Effects
- Fever or chills (20–50% during infusion)
- Nausea or vomiting (10–20%)
- Headache (5–10%)
- Anemia (5–10%)
These effects may decrease with pre-medication or lipid formulations.
Serious Side Effects
Renal: Reduced urine output, swelling, or elevated creatinine.
Electrolyte: Muscle weakness or irregular heartbeat (hypokalemia).
Cardiovascular: Hypotension or arrhythmias during infusion.
Allergic Reactions: Rare; rash, anaphylaxis, or bronchospasm.
Additional Notes
- Regular monitoring of kidney function, electrolytes, and blood counts is critical.
- Report any unusual symptoms immediately.
Drug Interactions with Amphotericin B
The medication may interact with:
- Nephrotoxic Drugs (e.g., Vancomycin, NSAIDs): Increase kidney damage risk; avoid or monitor closely.
- Corticosteroids: May enhance hypokalemia; monitor electrolytes.
- Digoxin: Risk of toxicity with hypokalemia; monitor levels.
- Flucytosine: Synergistic antifungal effect; adjust doses to avoid toxicity.
Patient Education or Lifestyle
Medication Adherence: Amphotericin B is administered by professionals; follow hospital treatment protocols and attend follow-up visits.
Monitoring: Report symptoms like fever, swelling, or hearing changes immediately. Regular blood tests are required.
Lifestyle: Stay hydrated to support kidney function; practice infection control to prevent fungal spread.
Diet: Maintain a balanced diet; avoid excessive potassium or magnesium unless prescribed.
Emergency Awareness: Know signs of renal failure (e.g., low urine output) or severe infusion reactions; seek immediate care.
Follow-Up: Schedule post-treatment tests to assess kidney and liver function.
Pharmacokinetics of Amphotericin B
Absorption: Not absorbed orally; administered IV for systemic effect.
Distribution: Volume of distribution ~4 L/kg; penetrates poorly into cerebrospinal fluid.
Metabolism: Not significantly metabolized; excreted unchanged.
Excretion: Primarily renal (<5% unchanged); some biliary excretion.
Half-Life: 15–24 hours (prolonged in renal impairment).
Pharmacodynamics of Amphotericin B
The antifungal exerts its effects by:
- Binding to ergosterol in fungal membranes, forming pores that cause leakage.
- Exhibiting broad-spectrum activity against yeasts and molds (e.g., Candida, Aspergillus).
- Demonstrating concentration-dependent killing, optimized with sustained levels.
- Effective against resistant fungi when susceptibility is confirmed.
Storage of Amphotericin B
Temperature: Store at 2–8°C (36–46°F); protect from light and freezing.
Reconstituted Solution: Use within 24 hours if refrigerated; do not freeze.
Safety: Store out of reach of children; restricted to hospital use.
Disposal: Dispose of unused vials per hospital protocols and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What does Amphotericin B treat?
A: The drug treats severe fungal infections like candidiasis or cryptococcosis.
Q: Can Amphotericin B cause kidney damage?
A: Yes, nephrotoxicity is a risk; report reduced urine output immediately.
Q: Is Amphotericin B safe for children?
A: Approved with adjusted dosing; monitor for toxicity.
Q: How is Amphotericin B administered?
A: Via IV infusion in a hospital by trained professionals.
Q: How long is Amphotericin B treatment?
A: Typically 2–6 weeks, depending on infection severity and response.
Regulatory Information
The medication is approved by:
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Approved in 1958 (Fungizone); later for lipid formulations.
European Medicines Agency (EMA): Approved for systemic fungal infections.
Other Agencies: Approved globally for equivalent uses; consult local guidelines.
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2023). Fungizone (Amphotericin B) Prescribing Information.
- Official FDA documentation detailing the drug’s approved uses, dosage, and safety.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). (2023). Amphotericin B Summary of Product Characteristics.
- EMA’s comprehensive information on the medication’s indications and precautions in Europe.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2023). Amphotericin B: MedlinePlus Drug Information.
- NIH resource providing detailed information on the drug’s uses, side effects, and precautions.
- World Health Organization (WHO). (2023). WHO Model List of Essential Medicines: Amphotericin B.
- WHO’s inclusion of Amphotericin B for fungal infections.
- Clinical Infectious Diseases. (2020). Amphotericin B in Invasive Fungal Infections.
- Peer-reviewed article on Amphotericin B efficacy (note: access may require a subscription).
